PCF Automation in 6 Steps
The calculation of a Product Carbon Footprint (PCF) is becoming increasingly important for many companies. Automation can be a real game changer here. These six steps show how to move effectively from a manual PCF assessment toward full process automation.
The calculation of product emissions — a Product Carbon Footprint (PCF) — is becoming increasingly important for many companies. With a wide product portfolio, this quickly turns into a major challenge.
Automation can be a real game changer here. To unlock automation potential within your organization, it helps to break the entire
1. Clarify the basics: What is reported, to whom, and based on which standard?
Before you move into the practical phase, you should be able to answer a few key questions:
- Who receives the PCF data — customers, authorities, or internal stakeholders?
- How should the data be presented — as a report, a digital interface, or an audit result?
- Which standards guide the reporting — GHG Protocol, ISO 14067, or other norms?
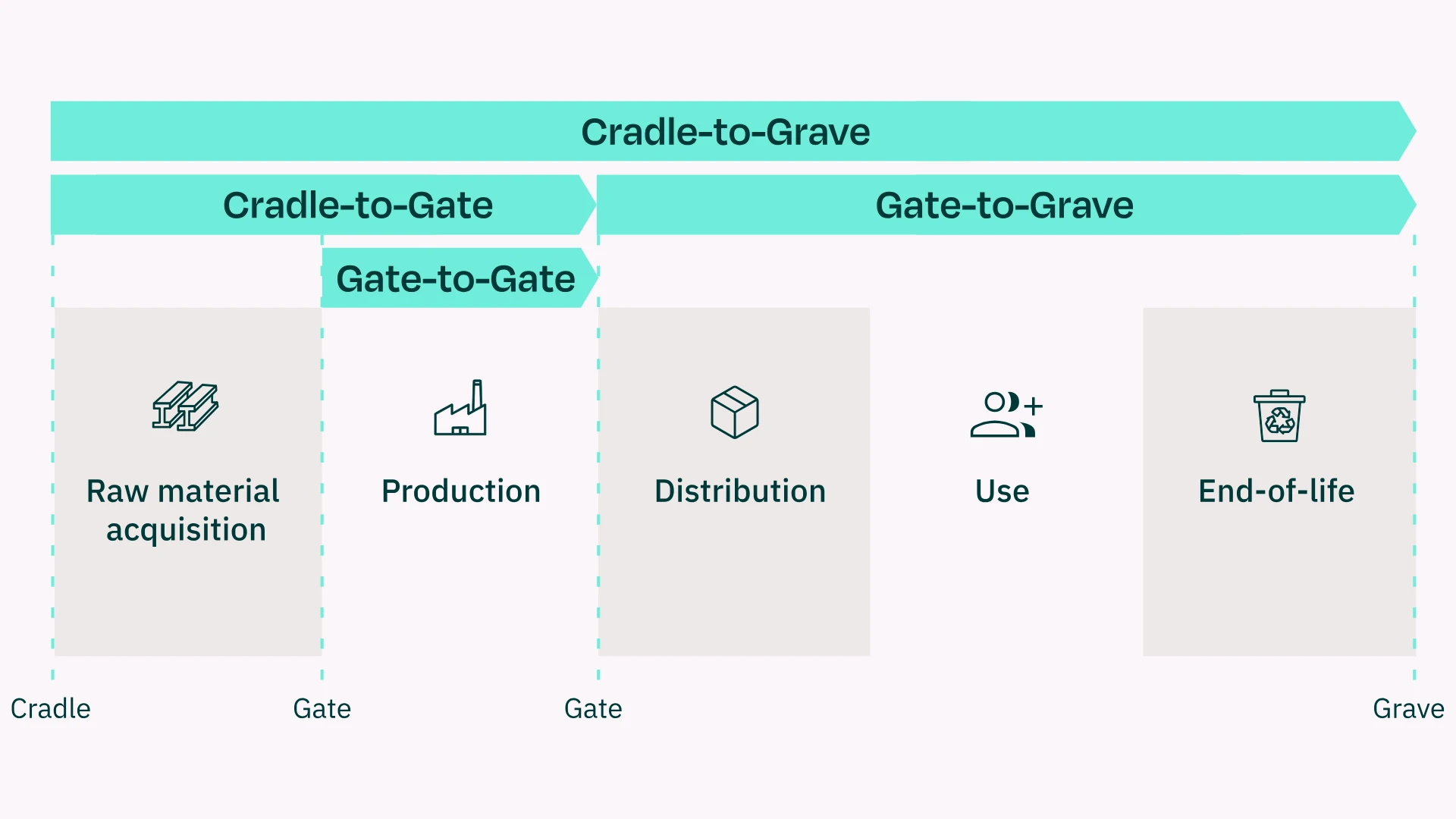
These questions define the methodological framework. They determine how deep the calculation needs to go (e.g., cradle-to-gate or cradle-to-grave) and which system boundaries apply.
2. Understand your role in the value chain
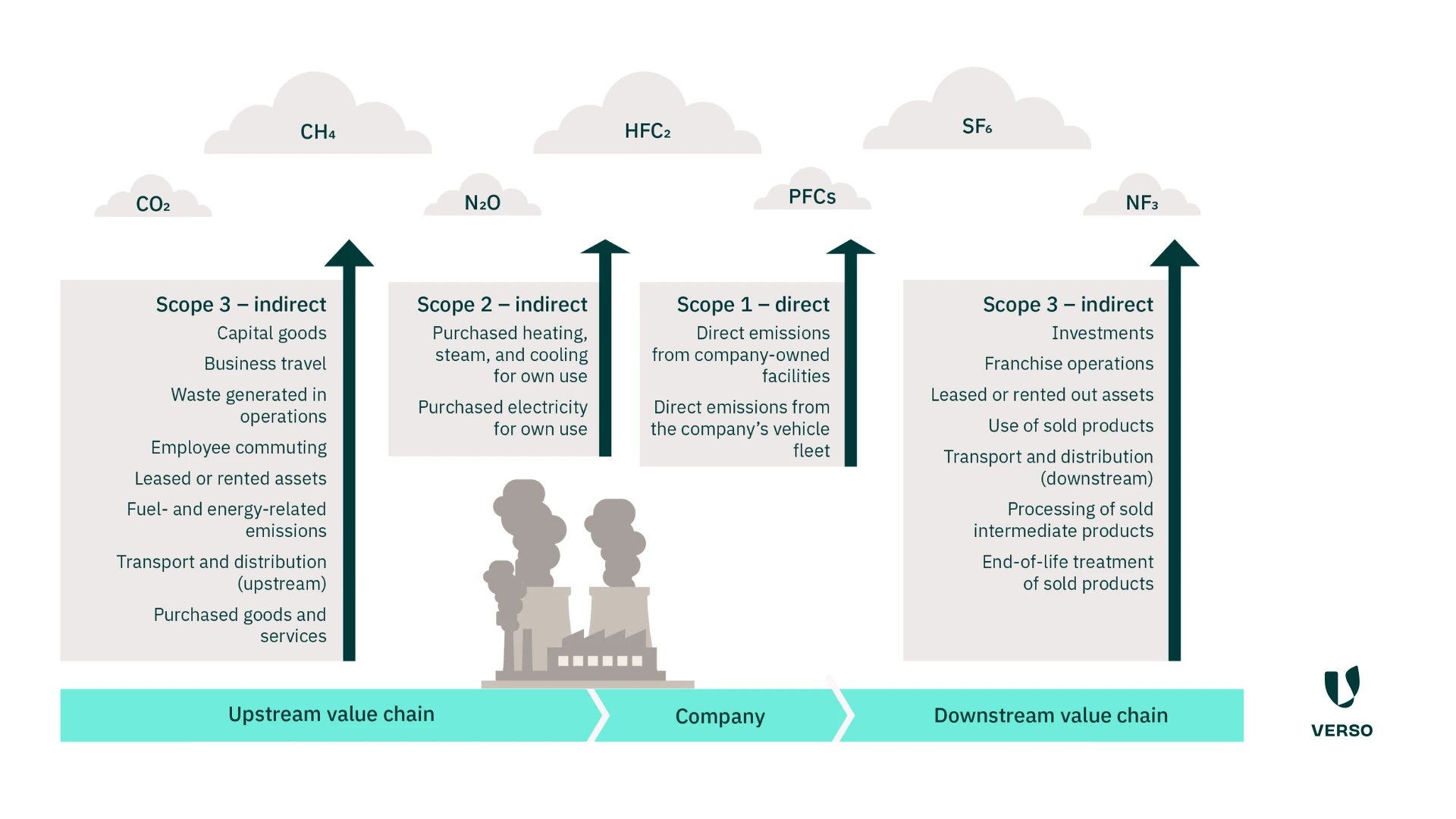
Your position within the value chain defines which data is relevant:
- Companies delivering to a single customer often need standardized downstream data.
- Companies at the end of the value chain must prepare information for final products and end customers.
- Suppliers in between need both: incoming data collection and outgoing data transmission.
This classification helps identify the right interfaces and automate them later on.
3. No automation without data quality
Automation depends entirely on the data foundation. Companies need to ask:
- Where do the data points come from — ERP systems, production data, supplier information?
- How can they be structured in a product-level and usable format?
- How can you ensure that the data is complete, consistent, and up to date?
Only when these questions are resolved is it worth moving toward technical automation. Otherwise, errors multiply instead of decreasing.
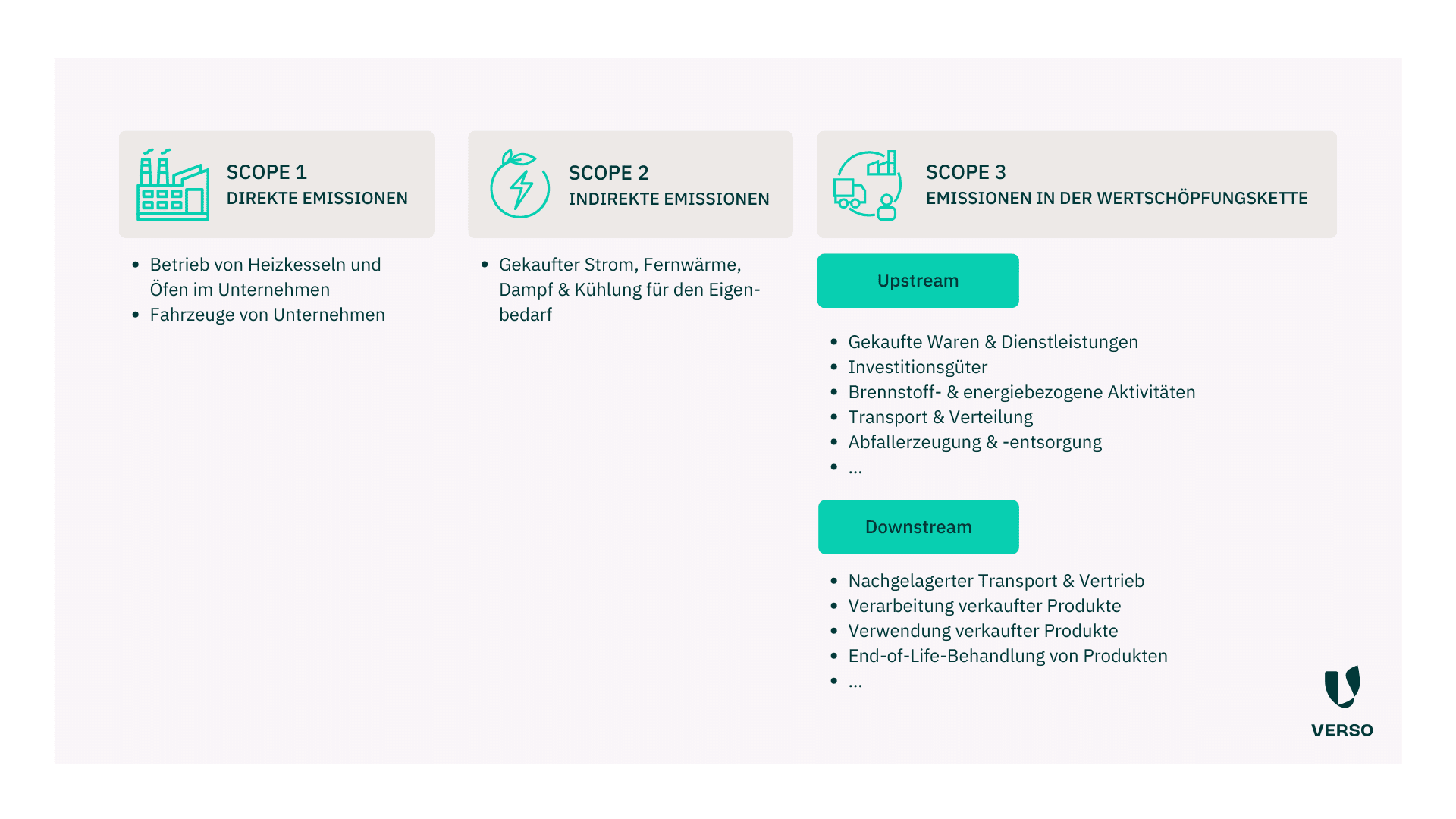
4. From databases to supplier data: Evaluate emissions correctly
A central step in calculating a Product Carbon Footprint is linking material data to emissions. There are two approaches:
- Emission factors from databases: easy to access, but based on averages.
- Factors based on data from your own supply chain: more complex, yet far more precise.
Many companies rely on databases in the short term. There are already many reliable sources with filtering options to find the most accurate factor possible. At VERSO, for example, we give you access to about 50 databases with over 200,000 emission factors.
In the long run, though, there is no alternative to supply chain data for real transparency and comparability. You should therefore request emission data or individual PCFs from your suppliers as soon as possible. You can also do this via the VERSO Supply Chain Hub. You then transfer the data directly into your PCF in the VERSO Climate Hub.
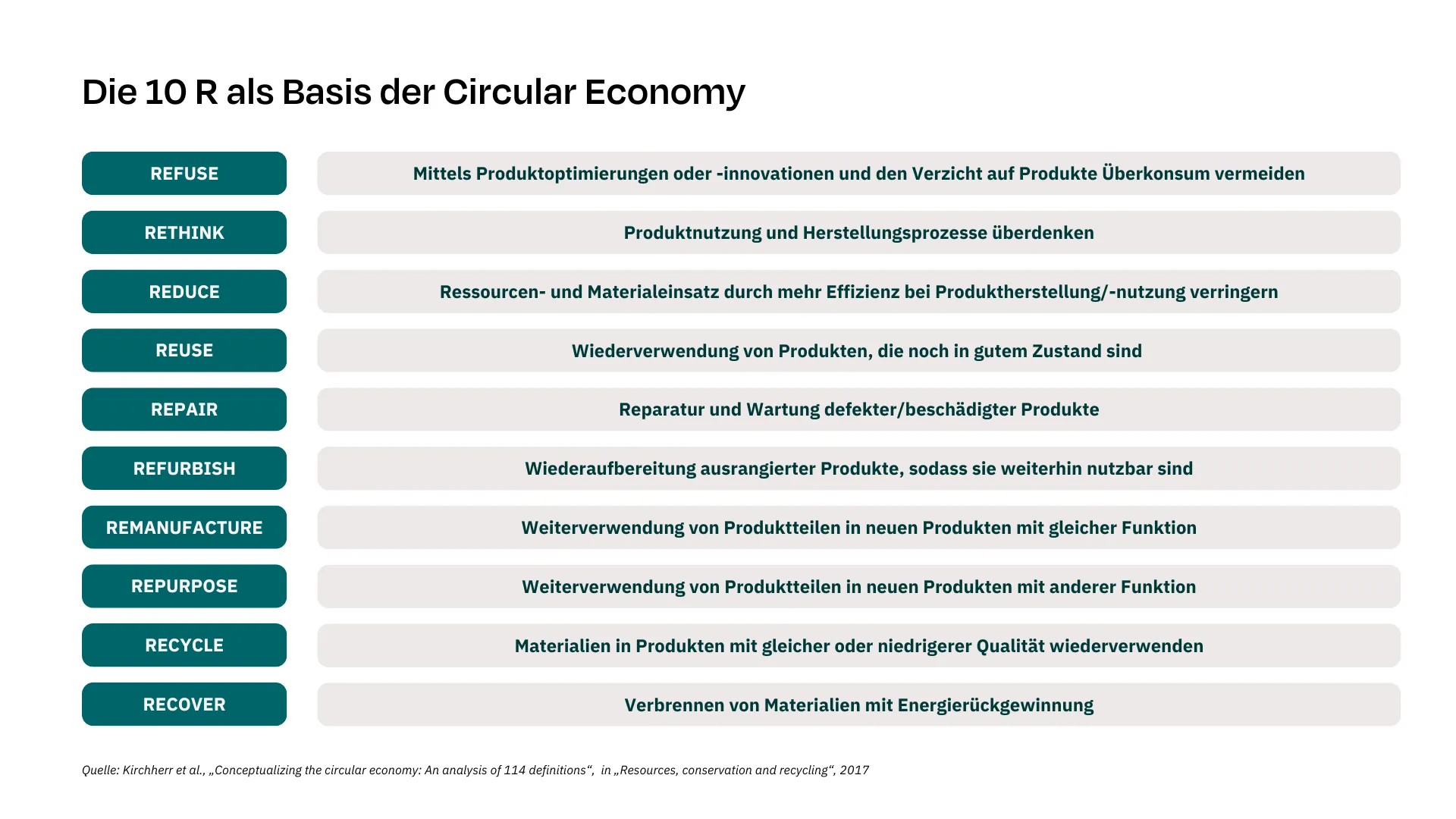
5. Automate step by step — instead of rushing ahead
Automation should definitely be the goal. However, many companies begin automating before the right foundations are in place. Often, materials are simply linked to emission factors — which may save time, but does not deliver reliable results.
A better approach: first build a solid methodological concept, structure processes in modules, and automate step by step. A modular system helps you start with a few well-defined processes. You can then transfer rules and calculation logic to additional products over time.
6. From partial to full automation
Once the methodology and data quality are right, automation can expand step by step:
- Automated data transfers between internal systems (ERP) and PCF software
- Intelligent and automated allocation of emission factors to materials
- Fully automated calculation processes
- Automated management and updates of emission factors
- …
The goal: end-to-end, reliable PCF calculations — without manual intervention.
This frees teams to focus on what matters: reducing emissions, implementing measures, and improving products.
Conclusion: Automate with intention
PCF automation succeeds when methodology and data quality come first. Clear goals, roles, and standards, structured data sources, and gradual automation lead to robust results with less effort. A modular approach supports automation, transparency, and comparability — all the way to end-to-end PCF calculation without manual input.
We are happy to support you with software and consulting.
* This information is summarized editorial content and should not be construed as legal advice. VERSO accepts no liability.
This might be also interesting for you:
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Sign up and receive regular news about:
- Current ESG topics and legislative changes
- Individual advice from the VERSO experts
- News about VERSO
- Sustainability Events and more