The history of the sustainability report: how it has evolved
The history of the sustainability report begins in the 1980s, when the first voluntary environmental reports were published. A lot has happened since then – right up to mandatory reporting. Read about the milestones and drivers that have shaped the ESG report and how the reports have developed in terms of depth and quality.
History of the sustainability report from 1980-2000: The era of environmental reports
The history of the sustainability report goes back to the 1980s.
But for the introduction to this blog article, let’s go back a little further.
This will help us to understand why the topic of sustainability and ESG suddenly became so popular.
Let’s transport ourselves back to the early 1970s, so to speak.
The world was characterized by rapid change and far-reaching social, economic and political developments.
The Cold War dominated international politics.
The oil crisis made people aware of their dependence on fossil fuels and their finite nature.
Economic growth and industrialization continued.
At the same time, however, environmental conditions deteriorated, for example due to polluted air and water. It was precisely at this time that a book was published that attracted worldwide attention.
The title: “The Limits to Growth”.
It was published by the Club of Rome, an association of scientists, economists, business people and former politicians.
This was a turning point.
The Club of Rome played a central role in ensuring that the issues of environmental awareness and sustainability were recognized globally for the first time.
But here we need to put the brakes on: not everything changed immediately.
Awareness was only gradually followed by action.
But there have already been the first Forerunner of the sustainability report.
In the 1980s, chemical companies published so-called environmental reports on their environmental activities.
These were voluntary and mainly served to improve their image, as the industry was subject to strong criticism.
In the 1990s, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) followed suit and became involved in environmental issues.
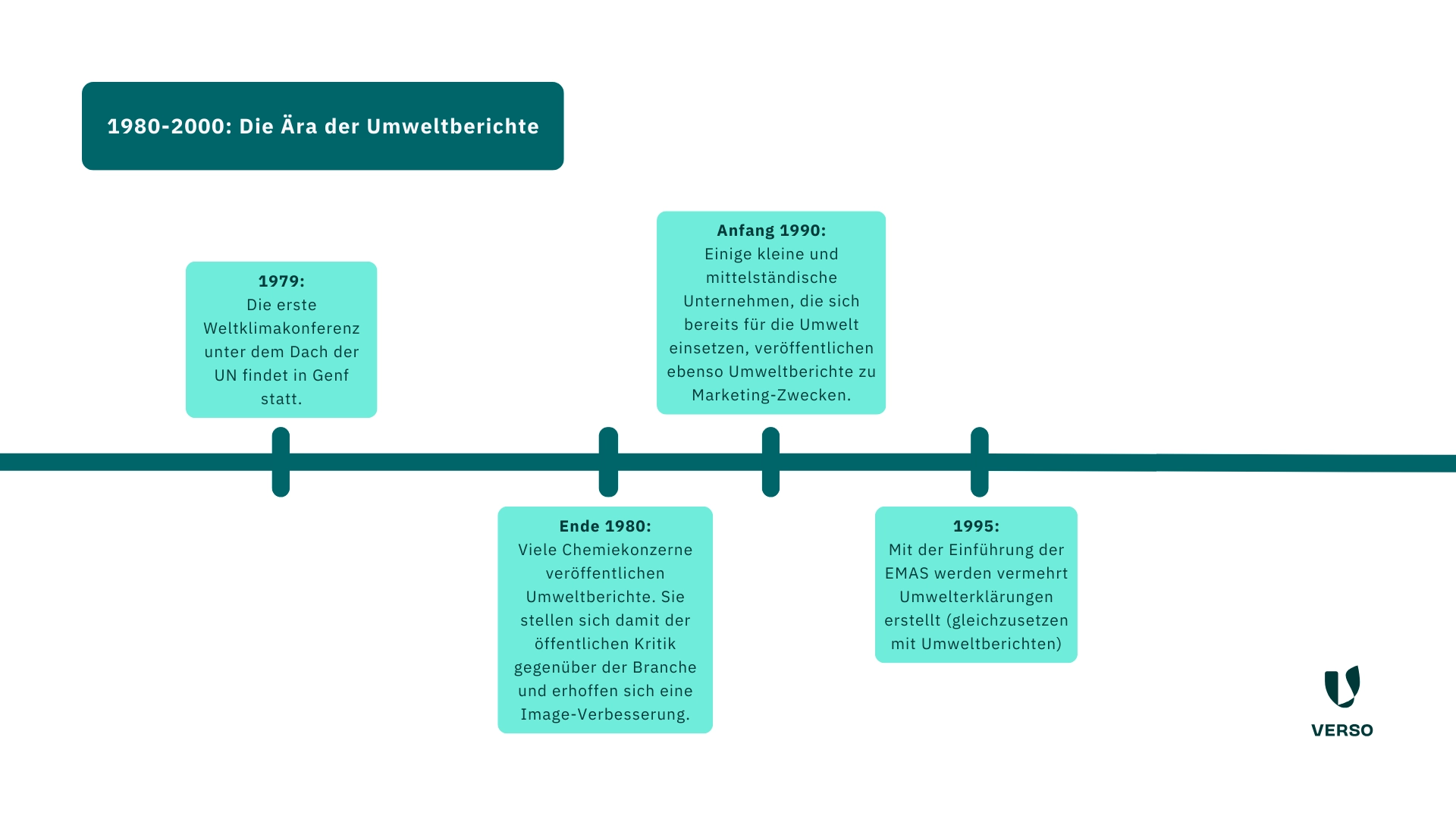
- 1979: The first world climate conference under the auspices of the UN takes place in Geneva.
- End of 1980: Many chemical companies publish environmental reports.
- Early 1990: Some small and medium-sized companies follow suit and also publish environmental reports for marketing purposes.
- 1995: With the introduction of EMAS, more and more environmental declarations are drawn up (equivalent to environmental reports).
History of the sustainability report from 2000-2010: Major corporations report
Our journey through the history of sustainability reporting continues with the turn of the millennium.
Compared to today, the attention paid to sustainability and ESG was manageable.
But there were important developments that brought it into the national and international spotlight.
The Kyoto Protocol was signed in 1997 and came into force in 2005.
It was the first international agreement to set binding targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
In 2002, Germany, like other countries, adopted a “National Sustainability Strategy”. In addition to public interest, new technologies also gave the topic of sustainability a boost.
At the turn of the millennium, wind power became the most important of all renewable energies.
Ten years later, it was replaced at the top by solar energy.
The overall advance of all renewable energies was unstoppable.
While the topic of sustainability itself gained in importance, this did not yet have a major impact on ESG reporting.
Until 2010, it was mainly large companies that published a voluntary sustainability report – they recognized the increasing attention for the topic.
However, two events provided a significant impetus here.
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) published its first guidelines.
They provided companies with a framework for reporting on environmental, social and economic aspects.
Over the years, the guidelines were further developed into the GRI Standards (from 2016).
The topic of sustainable finance also emerged.
Special indices were created with companies that act more sustainably.
Before the history of sustainability reports really picks up speed, let’s take a look at the most important milestones from this period:
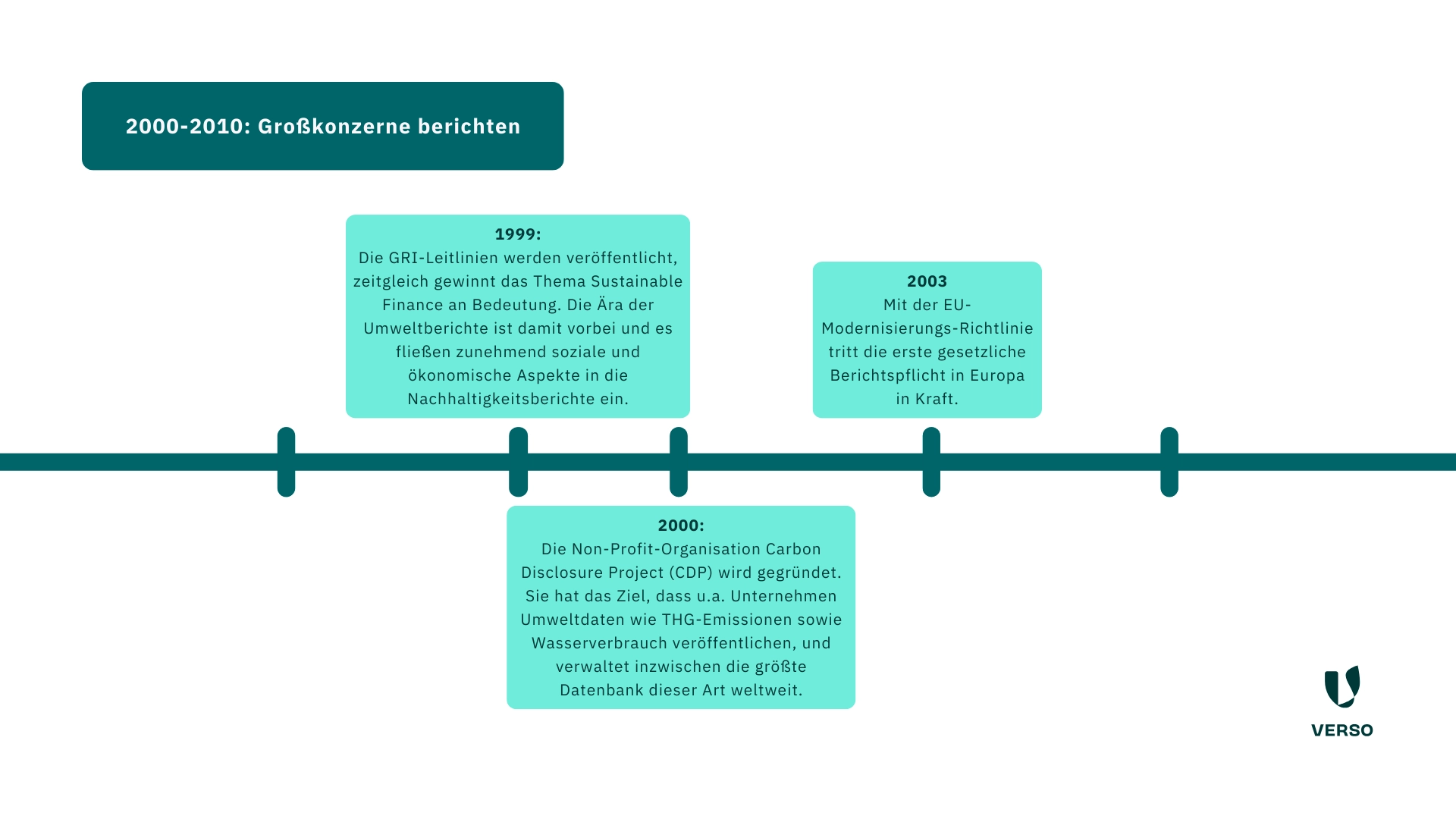
- 1999: The GRI guidelines are published, at the same time the topic of sustainable finance gains in importance.
The era of environmental reports is over and social and economic aspects are increasingly included in sustainability reports. - 2000: The non-profit organization Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) is founded.
Its aim is for companies to publish environmental data such as greenhouse gas emissions and water consumption, and it now manages the largest database of its kind in the world. - 2003: The first statutory reporting obligation in Europe comes into force with the EU Modernization Directive.
History of the sustainability report from 2014-2019: boom in frameworks
A veritable boom in ESG reporting regulations began in 2010.
This was accompanied by the development of numerous reporting standards and frameworks that offered companies a standardized method for disclosing sustainability aspects.
As a result, reports became more standardized and clearer and transparency increased.
A holistic view of sustainability was anchored in the standards.
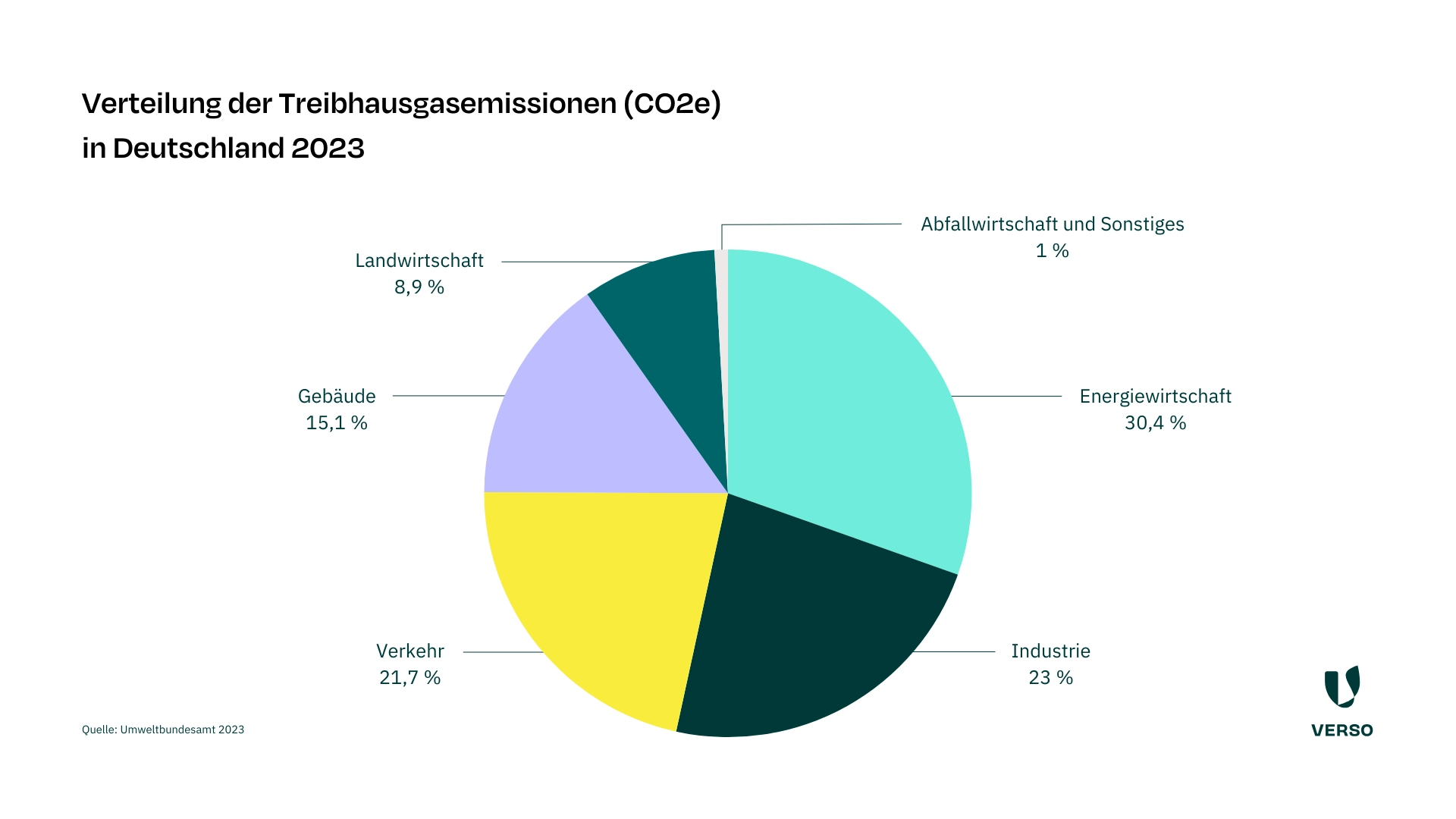
Typically, the environmental aspects were CO2 emissions, energy consumption and waste.
Social aspects included working conditions, human rights and communities.
Governance covered topics such as corporate management and ethical business practices.
Companies began to define and measure their sustainability goals and progress more clearly.
Many companies realized that sustainable practices are not only good for their image.
They can also bring economic benefits, such as cost savings, risk reduction and an improved competitive position.
You can read about the business value that sustainability can bring in the blog post“Why is sustainability important for companies?”. As this decade draws to a close, we would also like to look at a few highlights.
This time it’s about important frameworks and regulations:
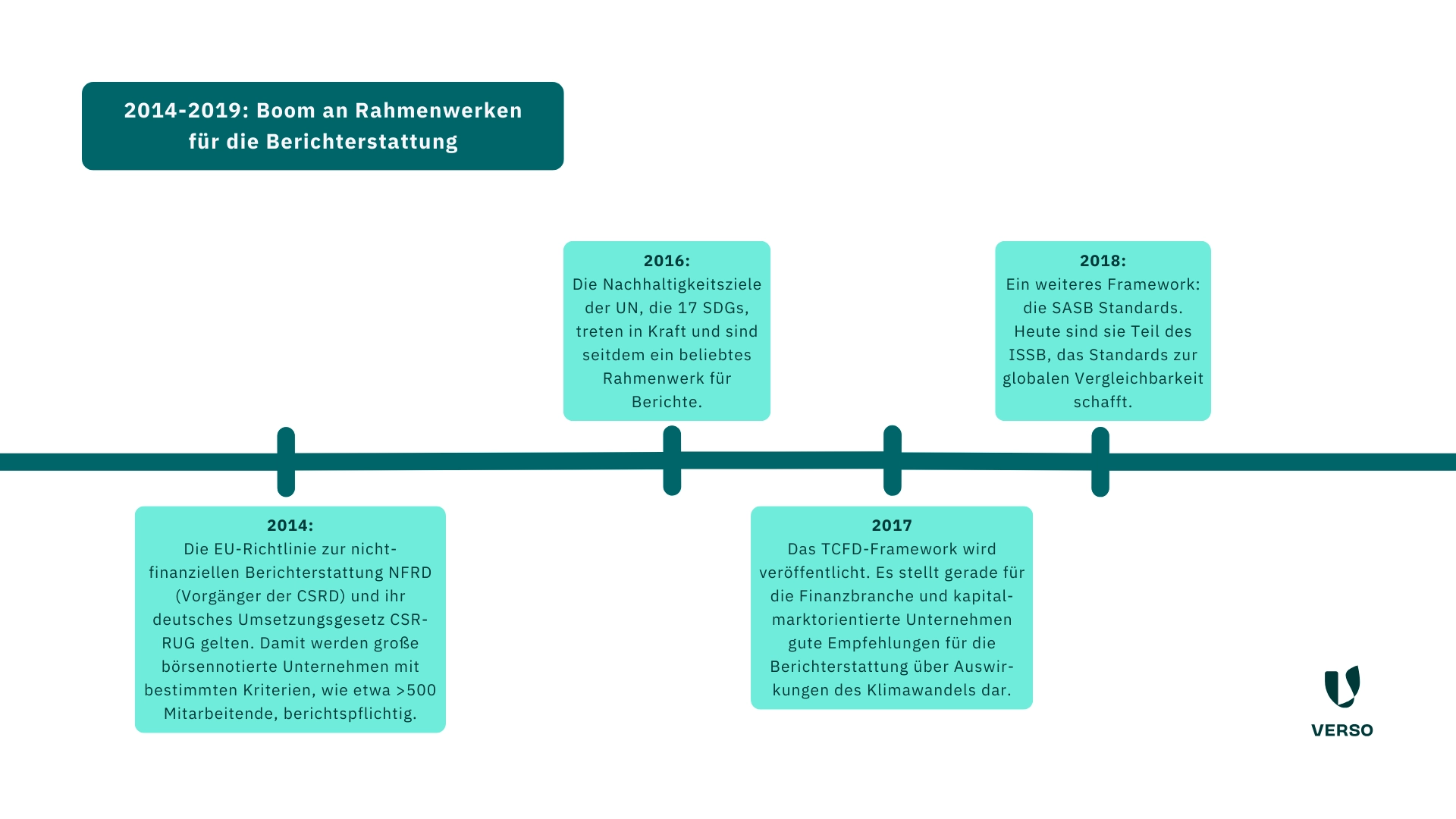
- 2014: The EU Non-Financial Reporting Directive NFRD (predecessor of the CSRD) and its German implementation law CSR-RUG (followed in 2017) come into force.
This means that large listed companies with certain criteria, such as over 500 employees, are required to report. - 2016: The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals, the 17 SDGs, come into force and have been a popular framework for reports ever since.
- 2017: The TCFD framework is published.
It provides good recommendations for reporting on the effects of climate change, particularly for the financial sector and capital market-oriented companies. - 2018: Another framework: the SASB standards.
Today, they are part of the ISSB, which creates standards for global comparability.
By the way: If you need an overview of standards and frameworks, take a look at our factsheet.
History of the 2019-2024 Sustainability Report: The EU and the Green Deal
The story of the sustainability report is now slowly coming to an end.
But only in this blog post.
A lot will certainly happen in this area in the coming years.
However, we don’t want to speculate, but rather take a closer look at what has happened since 2019.
The initial situation: there was a reporting obligation.
However, this only affected around 500 companies in Germany.
Companies had some freedom in the information they provided.
The main criticism was the poor comparability.
The new approach: With its Green Deal, the EU not only wanted to optimize and standardize ESG reporting, but also drive forward the entire sustainable transformation of the economy.
The central goal: Europe will be the first climate-neutral continent by 2050.
In order to implement this ambitious plan, the EU has put together a comprehensive package of directives and measures.
These included, for example, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the European Supply Chain Directive (CSDD).
As part of the CSRD reporting obligation, a standardized European framework, the ESRS, was even developed for the first time, which provides companies with clear guidelines regarding content and form.
Here is an overview of important regulations from recent years:
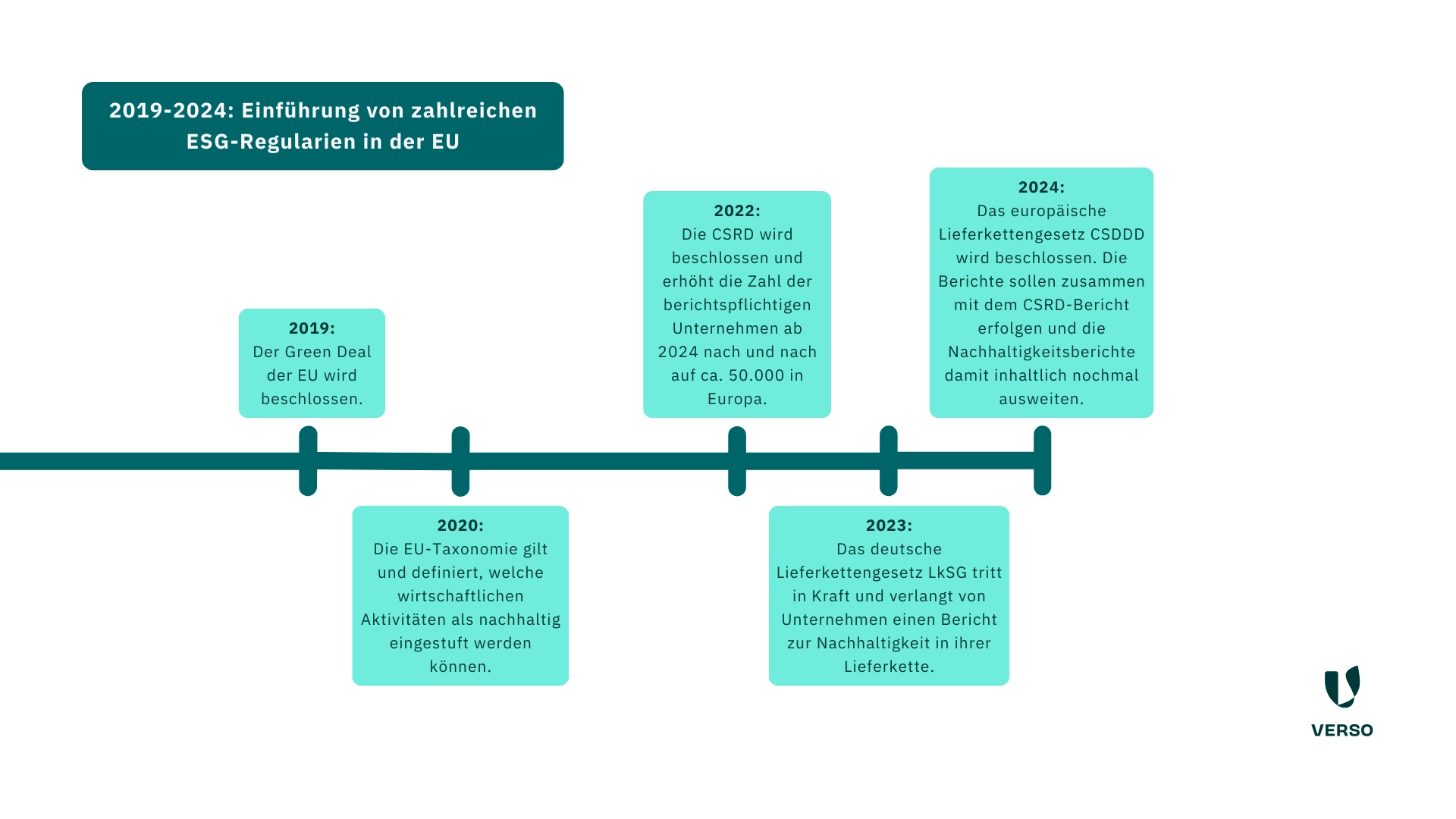
- 2019: The EU Green Deal is adopted.
- 2020: The EU taxonomy applies and defines which economic activities can be classified as sustainable.
- 2022: The CSRD is adopted and gradually increases the number of companies subject to reporting requirements from 2024 to around 50,000 in Europe and around 15,000 in Germany.
- 2023: The German Supply Chain Act LkSG comes into force and requires companies to submit a report on sustainability in their supply chain.
- 2024: The European supply chain law CSDDD is passed.
The reports are to be submitted together with the CSRD report, thus further expanding the content of the sustainability reports.
This might also interest you:
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Sign up and receive regular news about:
- Pragmatic all-in-one solution for ESG reporting, climate and supply chain management
- Individual advice from the VERSO experts
- Developed with expertise from 12+ years of sustainability management
- Trusted by 250+ customers