How the circular economy works and what it can achieve in Germany
Circular economy and circular economy are terms that you come across more and more often in the context of sustainability. What is behind them, why is the circular economy presented as an important system change and what would it look like in everyday life?
Circular Economy and circular economy are terms that you come across more and more frequently in the context of sustainability.
What is behind them, why are Circular Economy as an important system change and what would that look like in everyday life?
We have for you a brief insight with the most important topics compiled.
One really small. Dbecause the whole is so ramified and comprehensive that we could probably write a whole book about it.n couldnten
Circular economy and circular economy – what are they?
Circular economy and circular economy – what are they?
Let’s start with a classic definition.
Because – spoiler – the terms “Circular economy” and “Circular Economy” are often used synonymously, but are strictly speaking different.
Circular Economy
Circular economy describes an economic model in which resources and products are used for as long as possible within a closed cycle.
Once they have reached the end of their useful life, they are not simply disposed of, but returned to the cycle – i.e. made usable again.
The reference point is ISO 59004:2024.
It describes the basic principles and concepts of the circular economy, but also provides assistance for implementation in the company.
Circular economy is defined here as:
“Economic system that takes a systemic approach to maintaining the cycle of resources by recovering, preserving or enhancing their value while contributing to sustainable development.”
The WWF‘s definition is somewhat clearer and more direct:
“‘Circular Economy‘ [ist] a regenerative system, powered by renewable energy, which replaces the current linear industrial model ‘Take – produce – dispose‘ replaced.
Materials are instead retained in the economy, products are shared, while waste and negative impacts are avoided.
CE creates positive effects and benefits for the environment and society and works within planetary boundaries.
It is made possible by rethinking the current understanding of growth and consumption.”
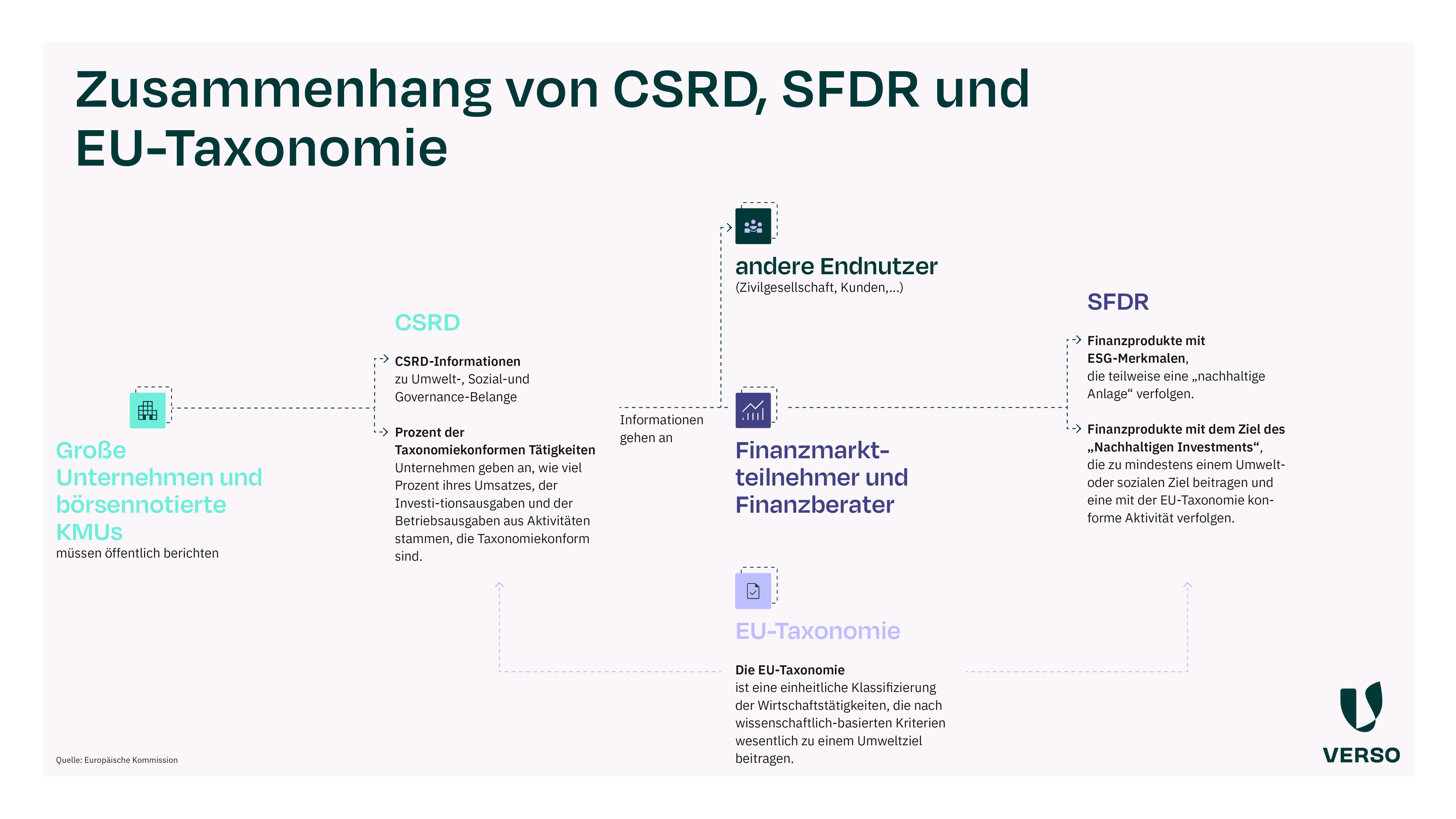
A helpful overview of all relevant standards relating to the circular economy can be found at the German Institute for Standardization (DIN).
For companies subject to CSRD, ESRS E5 (Resource use and circular economy) is also important in this context.
Circular economy
“Circular economy“ means exactly the same thing in theory.
In Germany, however, the circular economy actually only means avoiding waste: “The circular economy within the meaning of [the Circular Economy Act] is the prevention and recycling of waste“.
If we talk about the circular economy here in Germany, the correct term would be “circular economy”.
After all, we like to make life difficult for ourselves with unwieldy terms.
However, when the term “circular economy” is used at EU level (e.g. on the website of the EU Commission or EU Parliament), it always refers to the circular economy in the true sense of the word.
Why do we need a circular economy?
Global consumption of raw materials has tripled since 1970.
We live and do business as if we had unlimited resources at our disposal.
Earth Overshoot Day – the day on which all resources are used up globally for the year – is taking place earlier and earlier.
What is no longer needed is disposed of and replaced by something new.
And then it disappears from the scene for us.
But it ends up somewhere else.
Europe exports around 3,000,000 kilograms of plastic waste to countries in the Global South every day.
This is sometimes referred to as “Garbage colonialism” labeled.
And it doesn’t stop with plastic.
Growing mountains of old clothes, scrap metal, batteries, tires – our waste is piling up in other parts of the world.
On top of this comes the extraction of ever more resources for products that are produced in abundance worldwide.
Far too often, extraction and production go hand in hand with environmental damage and the violation of human rights.
The CSRD and supply chain directives such as the LkSG, CSDDD, CBAM and EUDR are intended to gradually prevent the latter.
However, what we actually need is a new economic system that tackles the underlying problems at the root.
Curtain up for circular economy.
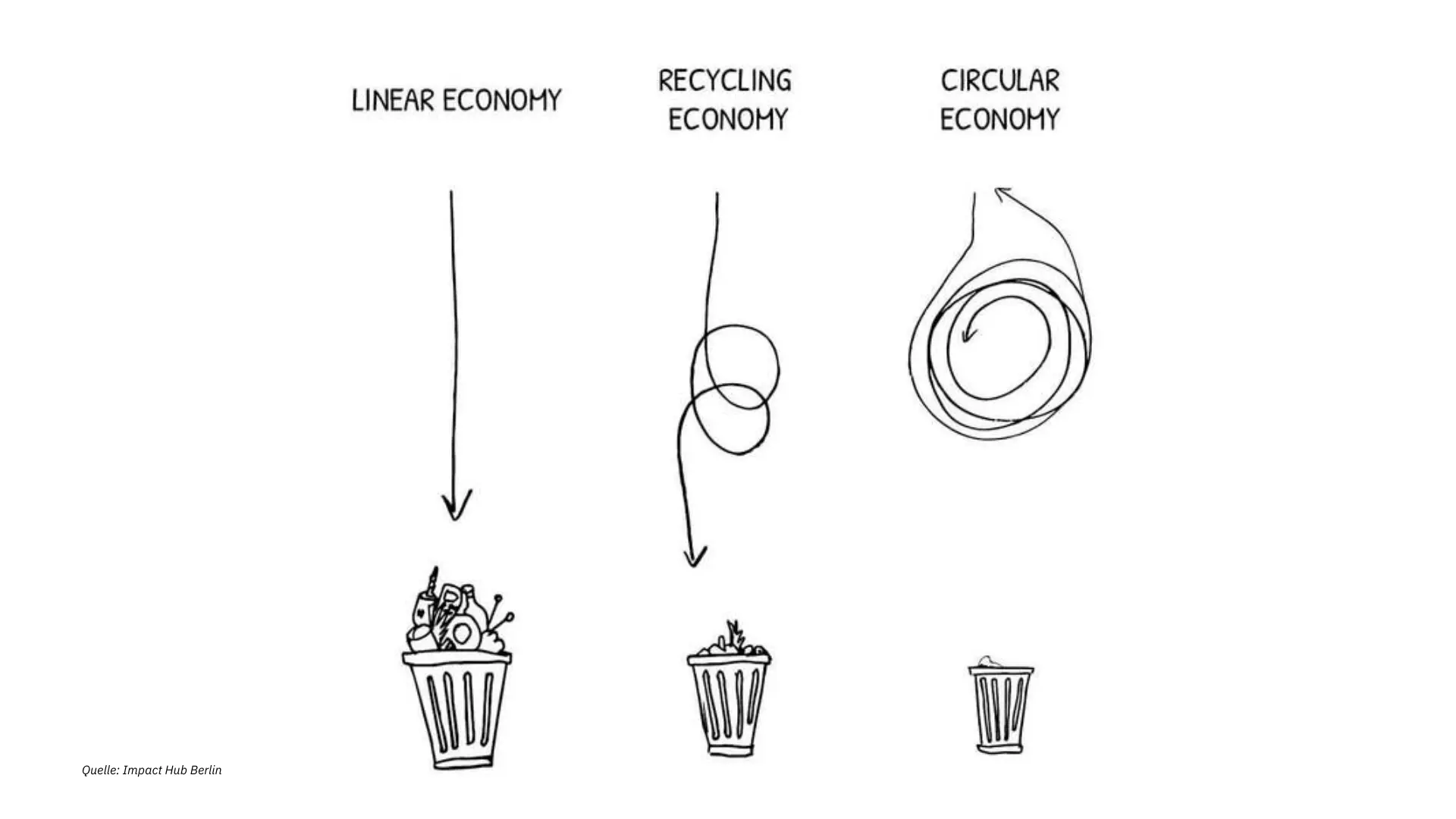
Linear Economy vs. Recycling Economy vs. Circular Economy – from the 3 Rs to the 10 Rs
Our current economic system is a one-way street.
It is therefore also known as “linear economy”.
There are already initial attempts to counteract the high consumption of raw materials and the throwaway mentality.
The focus here is on currently mainly on the so-called 3 Rs:
- Reduce – Reduce use of resources and materials through greater efficiency in product manufacture/use
- Reuse – Reuse of products that are still in good condition
- Recycle – Reuse materials in products of the same or lower quality
This gives rise to the recycling economy.
However, recycling only puts a slight damper on things.
In the end, there is still far too much waste piling up in mountains of garbage.
Only 7.2 percent of our materials are reused after use.
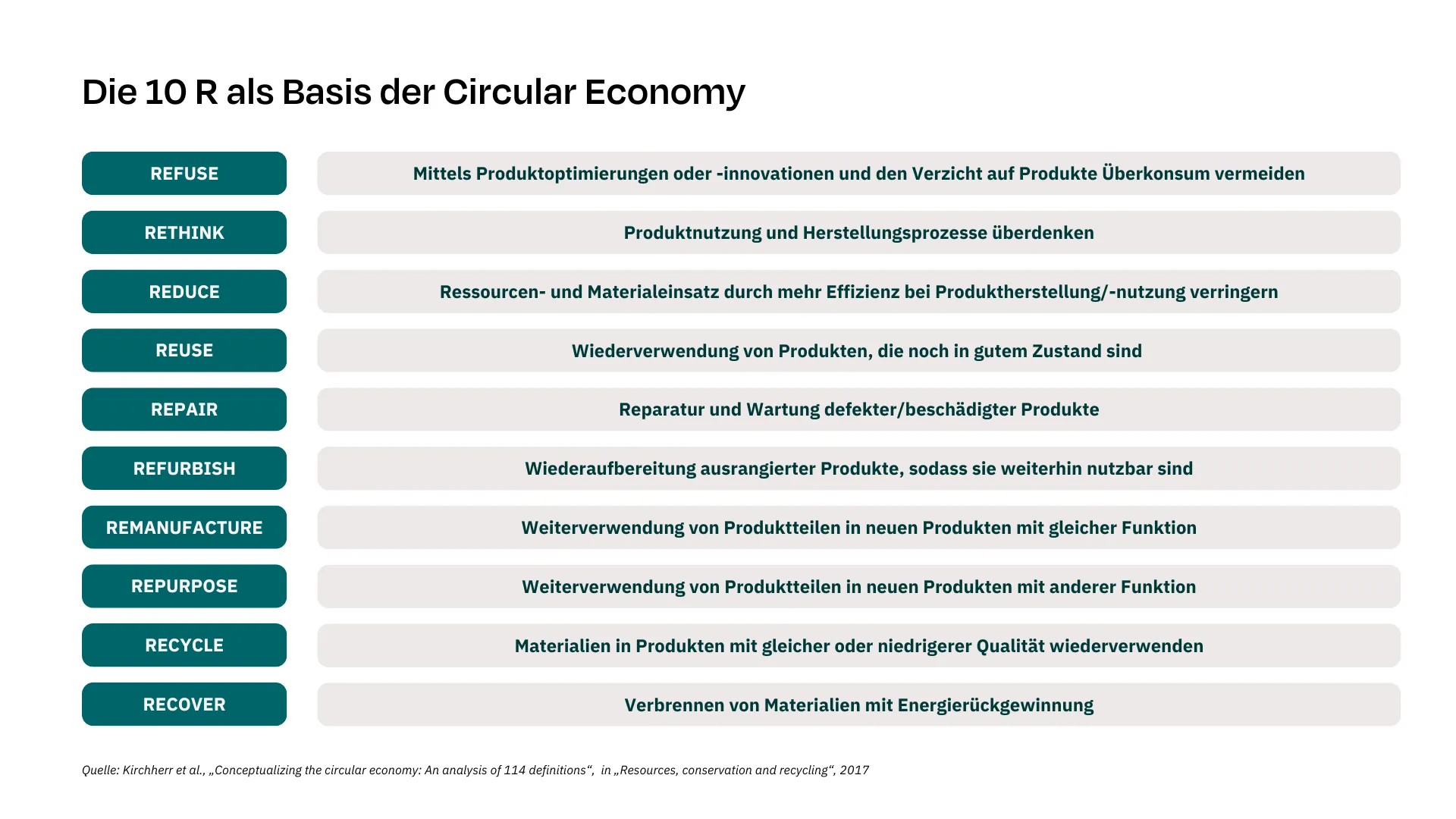
Circular Economy goes a big step further and relies on 10 R:
- Reduce – Reduce use of resources and materials through greater efficiency in product manufacture/use
- Reuse – Reuse of products that are still in good condition
- Recycle – Reuse materials in products of the same or lower quality
- Refuse – Avoid overconsumption by optimizing or innovating products and eliminating products
- Rethink – Rethinking product use and manufacturing processes
- Repair – Repair and maintenance of defective/damaged products
- Refurbish – Refurbishing discarded products so that they can still be used
- Remanufacture – Reuse of product parts in new products with the same function
- Repurpose – Reuse of product parts in new products with a different function
- Recover – Burning materials with energy recovery
The European Commission also lists 7 very similar pillars of the circular economy:
- Sustainable supply chains
- Ecodesign of products and services
- Industrial and territorial ecology, i.e. cooperation and exchange between companies
- Functional economic organization; i.e. sharing the benefits of products with others instead of owning your own products
- Responsible consumption
- Extend product service life
- Recycle
So much for the theory.
Now you’re probably asking yourself: what will it all look like in practice?
After all, a lot has to change for the circular economy to become a reality.
We need new processes and more durable, fully recyclable materials.
Not to mention a change in mindset.
Circular economy in practice
Action plan for the circular economy and national circular economy strategy
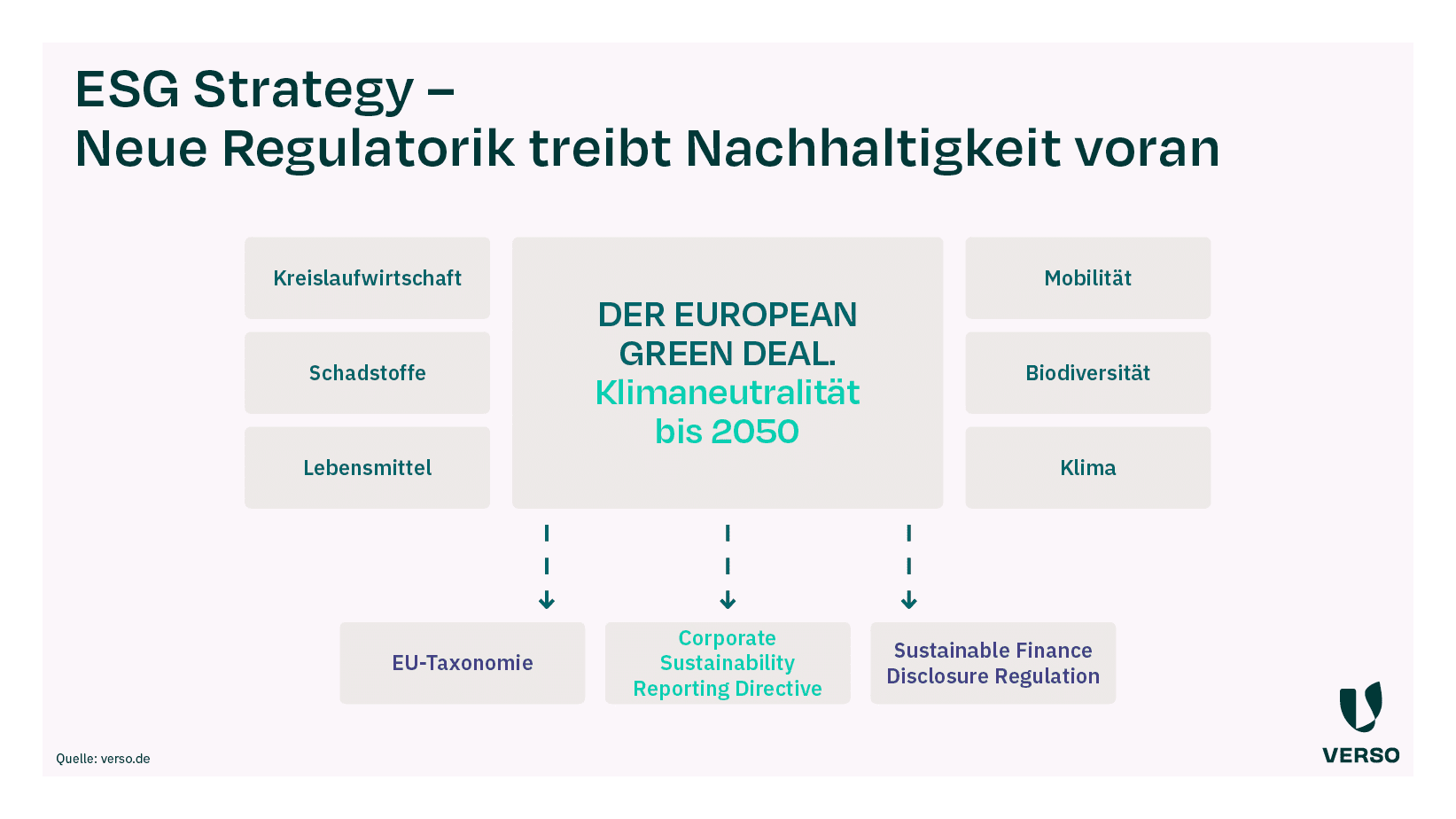
As part of the Green Deal, the EU 2020 has “Action Plan for the Circular Economy”, which aims to achieve a “carbon-neutral, ecologically sustainable and pollutant-free circular economy” by 2050.
Initial measures such as the extension of ecodesign regulations, the right to repair and the Green Claims Directive are already in force.
The “National Circular Economy Strategy (NKWS)” is based on the EU action plan.
This is intended to create a future framework strategy for measures and targets to implement a circular economy in Germany.
The German government is working closely with industry and society on this.
The overarching objectives of the NKWS are:
- Climate protection
- Protection of biodiversity
- Reducing species extinction and environmental pollution
- Securing the supply of raw materials
- Reduce GHG emissions
Model Germany Circular Economy
As the NKWS is still a work in progress, WWF Germany, together with the Öko-Institut, Fraunhofer ISI and the FU Berlin, has developed a roadmap for the circular economy in Germany – the “Model Germany Circular Economy (MDCE)“.
This comprehensive paper shows which measures, political strategies, targets and instruments could be used to achieve a circular economy by 2045.
Here is an overview of the most important findings.
The advantages of a circular economy compared to business as usual
- The supply situation is easing for 29 out of 36 critical raw materials, and for 9 raw materials more than 50 percent of Germany’s demand could be reduced or covered
- A CO₂-equivalent savings of up to 26 percent (186 million tons) are possible
- We need 27 percent less raw materials (179 million tons), total material consumption is down by 26 percent (329 million tons)
- We need 30 percent less land (8.5 million hectares)
- The MDCE scenario could also be used to reduce emissions that are difficult to avoid
- The modeled circular economy would avoid 26 percent (147 billion euros) of the climate damage costs caused by direct emissions – with indirect emissions 10.7 billion euros
What is currently hindering the circular economy
- Passing on environmental costs (externalization)
- Lack of infrastructure for circular products and processes
- Lack of investment (e.g. in research and development) for a circular economy
- Lack of transparency with regard to the transfer of information and data in the value chains
- Long-term path dependencies due to investments in linear technologies
- Lack of common standards for circular products
5 key strategies for implementing a circular economy
- Reduce resource flows
- Substitute materials
- Slowing down resource flows
- Intensify product use
- Closing resource cycles with high quality
Consumers, companies and politicians share responsibility
The circular economy must be considered from two perspectives:
- Behavior-based solutions – sustainable design of consumption
- Technology-based solutions – on the technical and production side
The paper emphasizes that the necessary changes in behaviour do not lie solely with consumers.
Both approaches require “political and entrepreneurial need for action that goes far beyond information instruments and should be controlled by regulatory and market-based instruments.“
10 guiding political principles for the success of the circular economy
- Prioritize absolute reduction of resource consumption
- Set binding resource targets along the lines of climate targets
- Shaping the structural change triggered by the circular economy with specific policy instruments
- Creating conviction for comprehensive CE in social alliances
- Understanding education and knowledge transfer as the key to transformation
- Setting incentives for a change in values in companies
- Expanding the state’s role model function in procurement
- Strengthening regional value chains in Germany
- Provide financing and research & development for the transformation to a circular economy
- Germany must assume greater international responsibility
Conclusion: We still have a long way to go!
Looking at our current economic model and the MDCE draft, it is clear that we still have a lot of work to do to achieve a truly sustainable transformation.
It can only succeed if we all – consumers, companies and politicians – work hand in hand.
Let’s get started!
Read more:
- Model Germany Circular Economy – Full paper with proposed measures for environmentally intensive sectors
- Circularity Gap Report 2024 – Information and roadmap for a global circular economy
- Information portal on the NKWS
- German Circularity Index 2024 – an overview of the circular economy progress of German companies
This might also interest you:
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Sign up and receive regular news about:
- Pragmatic all-in-one solution for ESG reporting, climate and supply chain management
- Individual advice from the VERSO experts
- Developed with expertise from 12+ years of sustainability management
- Trusted by 250+ customers