The EU ESG guidelines and how they relate to each other
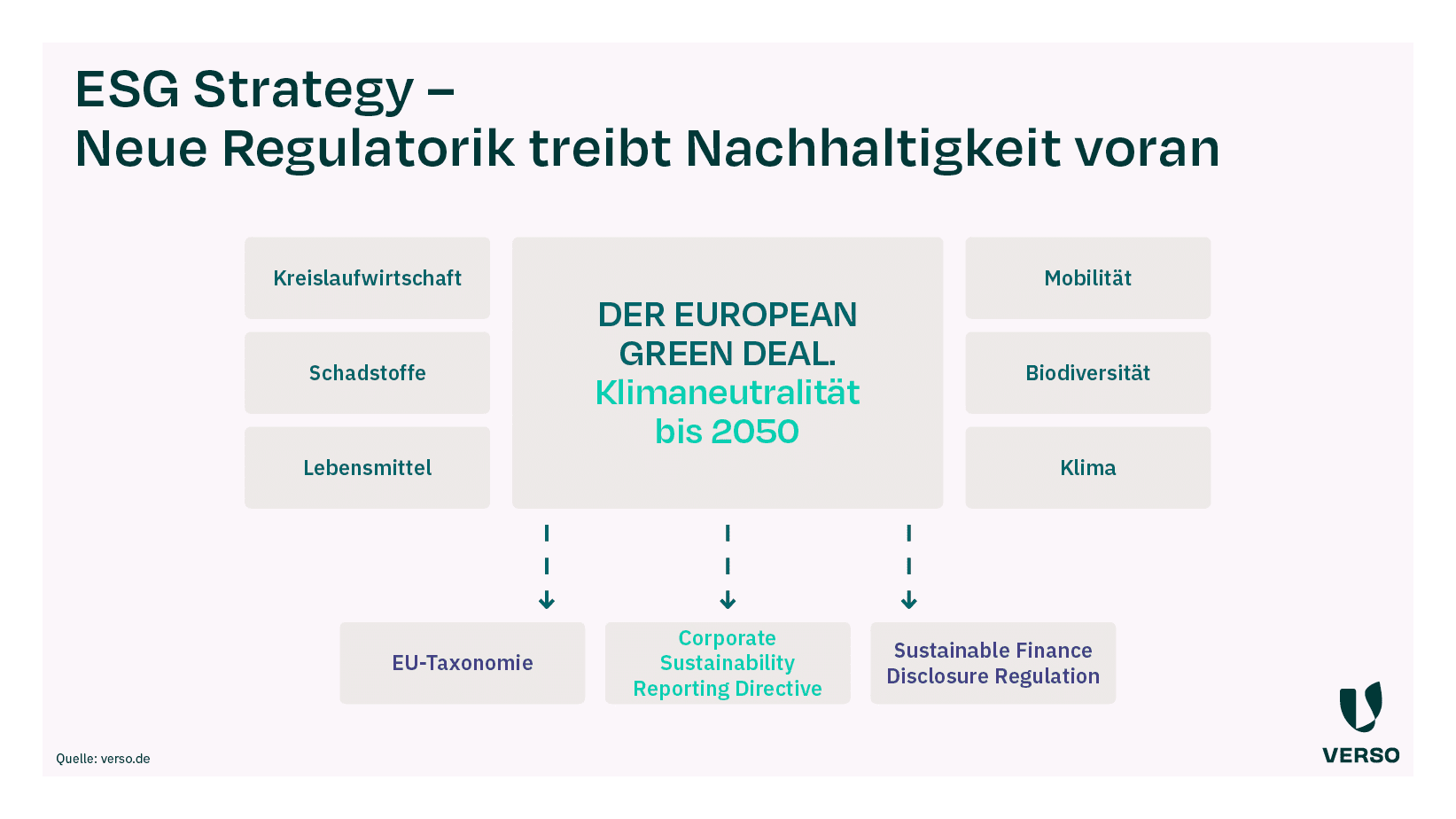
The European Union’s Green Deal
With its Green Deal, the European Union wants to make the EU climate-neutral by 2050 and channel financial flows into sustainable projects and companies.
The extensive program also includes three important ESG guidelines and regulations for sustainability reporting:
- EU taxonomy,
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and
- Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR).
But how are they connected and why are all three important for companies?
EU taxonomy, CSRD and SFDR briefly explained
Before we take a closer look at the relationship between the EU taxonomy, CSRD and SFDR, we will first look at the three EU requirements individually.
The European Union adopted the EU Green Deal back in 2019.
The program provides for extensive measures that penetrate deep into the economy and industry.
This also includes the three directives.
EU taxonomy
The EU taxonomy came into force on January 1, 2022 and defines which economic activities can be classified as sustainable.
The regulation sets out criteria for climate and environmentally friendly activities and products.
Accordingly, an economic activity must
- make a substantial contribution to at least one of the six environmental goals,
- do not compromise one or more of the other environmental objectives, and
- in compliance with the minimum protection (OECD Guidelines).
Further information can be found in our factsheet on the EU taxonomy.
CSRD
While the EU taxonomy focuses on activities and products, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive focuses on the company level.
The CSRD will be introduced in stages from 2024 and regulates sustainability reporting by companies.
Ultimately, around 15,000 companies in Germany and around 50,000 in the EU will be affected by the directive.
The CSRD creates a uniform framework for the disclosure of ESG (environmental, social and governance) data.
In this context, there is a binding reporting standard in the European Union for the first time: the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS).
Further information can be found in our factsheet on the CSRD.
SFDR
The Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation came into force on March 10, 2021.
It obliges financial market participants such as private equity, venture capital and fund companies as well as financial advisors to disclose sustainability information on their products and portfolios.
The increased transparency is intended to ensure that environmental and social factors are given greater consideration when making investment and financing decisions.
A commitment to “sustainable finance”, so to speak.
Further information can be found in our factsheet on the SFDR.
The relationship between the EU taxonomy, CSRD and SFDR
Transparency is crucial to channeling more money into sustainable projects and companies.
Customers, employees, investors and many other individuals and groups demand detailed information on environmental, social and governance (ESG) issues.
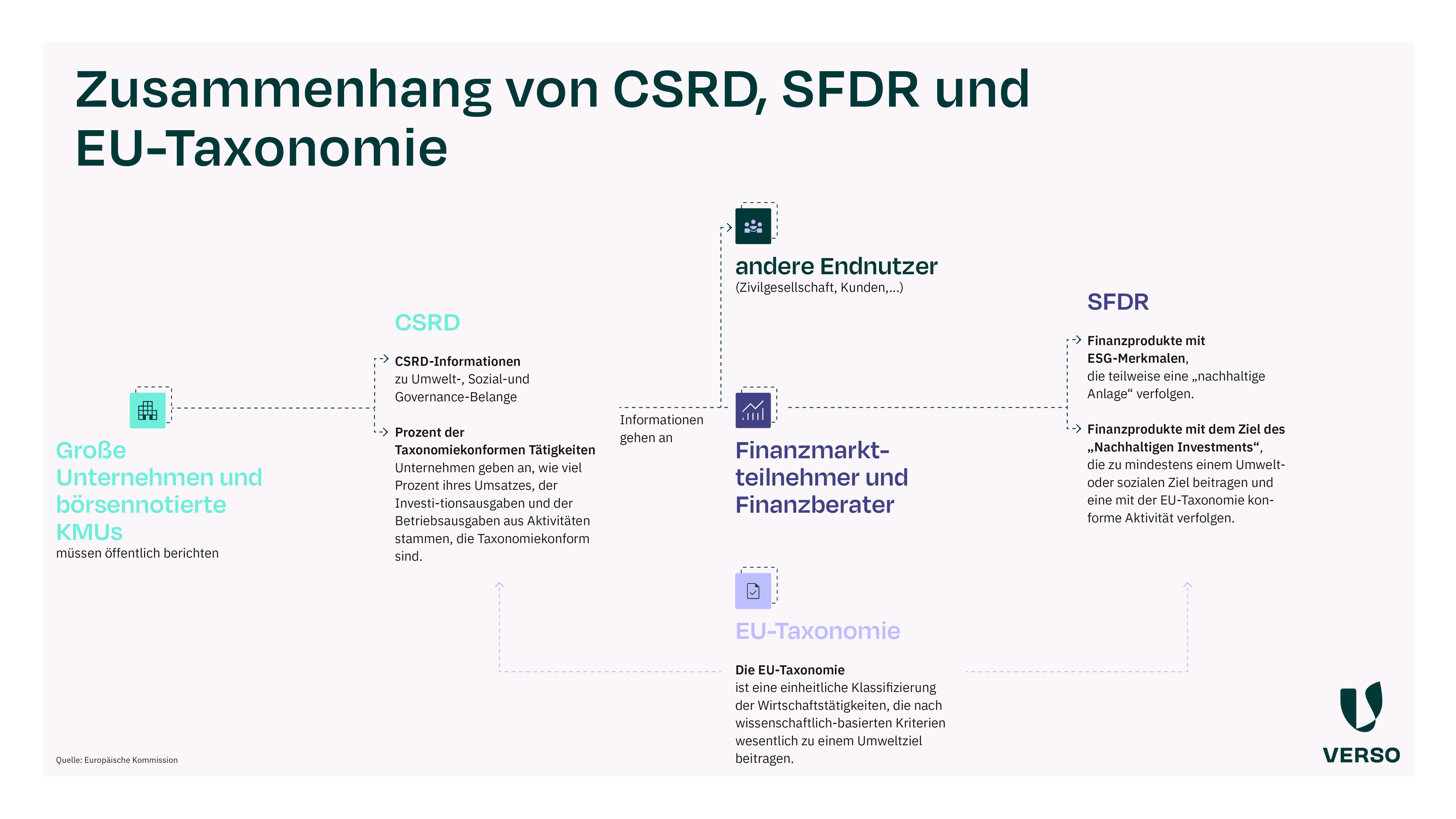
The interaction between the EU Taxonomy, CSRD and SFDR sets the framework for the disclosure of sustainability aspects.
The mutual relationships between the EU Taxonomy, CSRD and SFDR can be clearly seen in our illustration.
As you can see, the three sets of rules are closely interrelated and even overlap in terms of content.
First of all, the EU Taxonomy provides a classification system for sustainable economic activities, which is applied within the framework of the CSRD and SFRD.
The CSRD obliges companies to report on various ESG aspects.
Affected companies must also provide information on three key indicators of the EU taxonomy – namely the proportion of taxonomy-eligible economic activities
- of total sales
- in capital expenditure (CapEx) and
- operating expenses (OpEx).
The EU taxonomy and CSRD also play a role in the SFDR.
Financial market participants and financial advisors must report on key figures from the EU taxonomy for their ESG financial products that promote environmental or social characteristics or have a completely sustainable investment objective.
This requires information on the proportion of a financial product that invests in taxonomy-compliant activities.
For example, information is requested on greenhouse gas emissions, consumption and production of non-renewable energy, wage differences and gender diversity.
The financial service providers in turn obtain this sustainability-related information from the CSRD reports of the companies in which they invest.
However, there is currently a certain amount of tension.
The CSRD, i.e. the obligation to prepare a sustainability report, does not yet apply to many companies.
It will be introduced in stages from 2024.
The group of companies subject to reporting requirements will only gradually expand from 2025.
However, due to the SFDR, many companies already have to report sustainability information to financial market participants if they require a loan or investment.
It is therefore clear that it is worthwhile for companies to start reporting and collecting data at an early stage.
Why is sustainability important for companies?
There are numerous reasons to make a company more sustainable.
Firstly, there is growing pressure from outside – from regulatory requirements, for example, but also from customers, business partners and competitors.
But current and potential employees are also paying more attention to how their (future) employer acts and whether this is compatible with their views.
Sustainability can therefore provide a competitive advantage, strengthen the brand, increase employee motivation, retain customers and create new jobs, among other things.
As we have seen above, it also helps in the search for investors.
And, of course, a company makes a contribution to protecting our planet.
You can find numerous studies that prove this in the blog post“Why is sustainability important for companies?”.
We support you with the ESG report
You should therefore start collecting the relevant sustainability information in your company at an early stage.
You can save yourself a lot of time and effort by using specialized sustainability software such as the VERSO ESG Hub.
Our sustainability experts will also support you throughout the entire reporting process – from the materiality analysis, strategy and carbon footprint to the final reporting.
* This information is summarized editorial content and should not be construed as legal advice. VERSO accepts no liability.
This might also interest you:
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Sign up and receive regular news about:
- Pragmatic all-in-one solution for ESG reporting, climate and supply chain management
- Best practices in the areas of ESG and sustainable supply chains
- Developed with expertise from 12+ years of sustainability management
- Sustainability events and much more.