Fit for CBAM: Key Facts and Requirements
As part of the EU’s climate strategy, the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) puts a price on CO2 emissions from goods imported into the EU from non-EU countries. The goal is to promote emission reductions and protect the competitiveness of EU industry. This article outlines what companies need to know to ensure CBAM compliance.
What is CBAM? A Brief Overview
CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) is the official name of EU Regulation 2023/956. It entered into force on 1 October 2023 and complements the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS). Together, they aim to reduce emissions from both goods produced within and imported into the EU.
Objectives of CBAM:
- Strengthen existing emission reduction measures
- Encourage companies to reduce emissions rather than relocate production
- Protect EU-based companies from cost-related competitive disadvantages
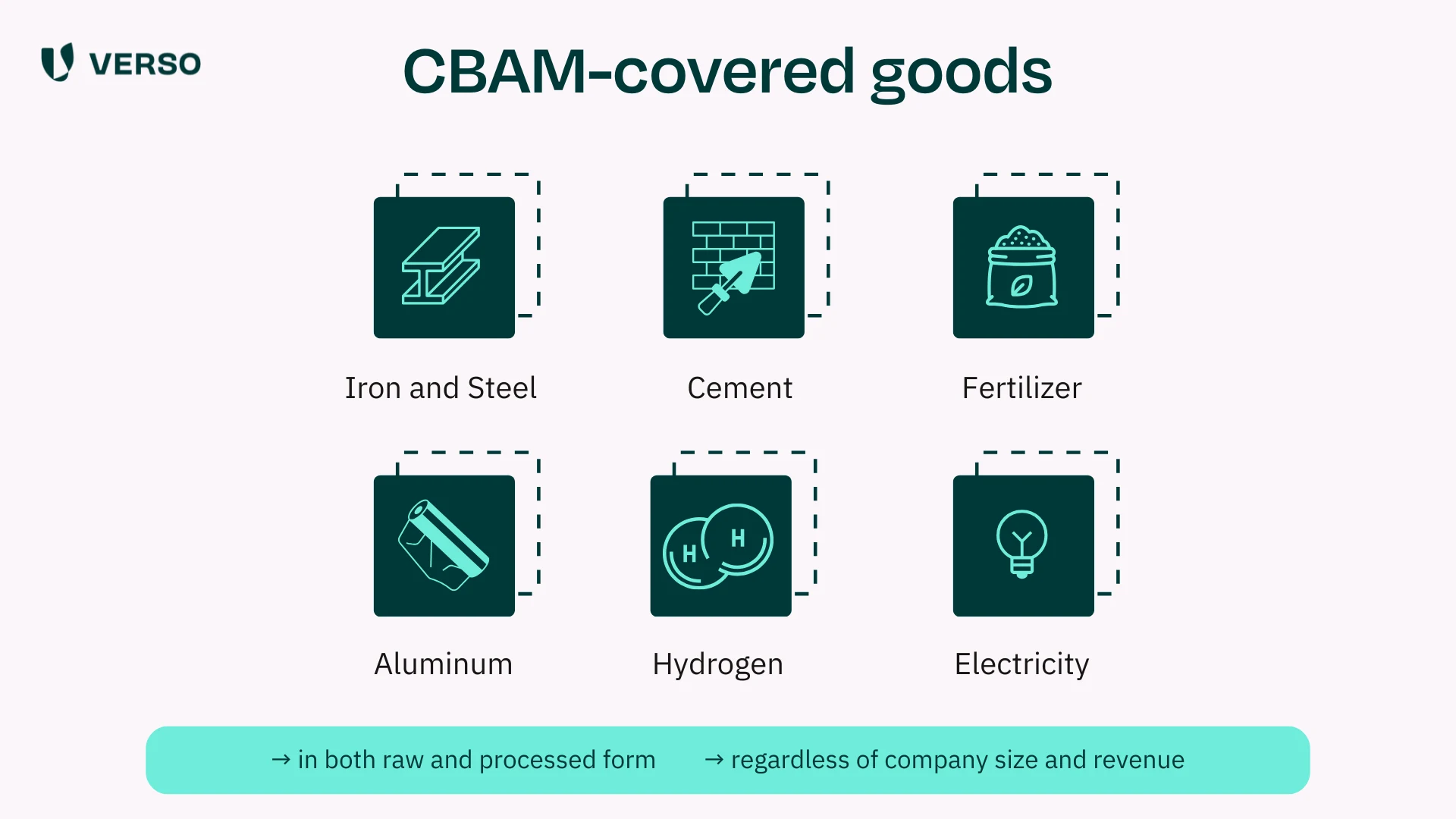
Annex I of the CBAM regulation lists the relevant CN codes in detail.
The EU plans to expand the scope of CBAM. By 2030, all products covered under the EU ETS are expected to be included.
CBAM Reporting and Certificates: Deadlines and To-Dos
Since 2023: Quarterly reporting (reporting obligation)
Reports must be submitted within one month after the end of each quarter and include:
- Company master data
- CBAM account number
- Quantity and type of imported goods
- CBAM-relevant greenhouse gas emissions
- Specific emissions, not default values
- Covers both direct production emissions and indirect emissions from the production of inputs or required electricity
- CO2 price paid in the country of origin
From 2026: Certificate trading and annual CBAM declaration
Starting 1 January 2026:
- Emissions not offset in the country of origin must be covered using CBAM certificates
- A CBAM registration is required for each company location
- Certificates can be purchased via a central platform at a price based on the weekly average of EU ETS certificates
- Companies must have enough certificates to cover at least 80 percent of their imported CBAM emissions. VERSO’s Supply Chain Hub helps with calculation and tracking
Important: From 2026, only authorized declarants are allowed to import CBAM goods and purchase certificates.
From 31 May 2026:
The quarterly report will be replaced by the annual CBAM declaration. Due by 31 May of the following year (i.e. the 2026 report is due on 31 May 2027) and must include:
- Total volume of imported goods
- Total embedded emissions by product group
- Number of CBAM certificates used, minus CO2 prices paid abroad
CBAM FAQ
Where do I submit CBAM reports?
Reports are currently submitted via the CBAM transitional registry, which you should be able to access via your national customs portal.
Are there penalties for non-compliance with CBAM?
Yes. The regulation allows for proportionate and dissuasive penalties. Even during the transition phase, fines between 10 and 50 euros per tonne of unreported CO2 emissions may apply.
Are there thresholds for CBAM reporting?
Yes. Reporting only applies to imports with a customs value above 150 euros per shipment. Otherwise, CBAM applies in full.
Can I still use default values in the report?
From 31 July 2024, default values may no longer be used. If you do not yet have real emissions data (e.g. from suppliers), Germany’s Emissions Trading Authority may still allow temporary use of default values if:
- You document your approach to obtaining real data
- You demonstrate that you made reasonable efforts to collect the data
- You provide your explanation in the “Comments” field of the transitional registry
Your submitted report must be internally consistent – review it carefully.
Will the Omnibus proposal change anything?
Yes, the Omnibus proposes several changes to ease CBAM implementation, including:
- New import threshold of 50 tonnes per company per year; CBAM only applies above this limit
- Flexible choice between default values (with a surcharge) or actual emissions
- Downstream production processes excluded from reporting
- Annual report deadline postponed to August
- Certificate obligation phase postponed to 2027
- Reduced certificate requirement from 80 to 50 percent
Tips for CBAM Implementation
CBAM compliance adds administrative effort – particularly around data collection. Close collaboration with suppliers is crucial.
Solutions like the our CBAM Module can support companies by automating data capture, monitoring emissions, managing certificates, and ensuring documentation.
Background knowledge on CBAM
In 2005, the EU ETS was introduced as the EU’s instrument to meet Kyoto Protocol targets. It has undergone multiple reforms – most recently in 2021 as part of the Fit-for-55 package.
The ETS operates as a cap-and-trade system: companies receive an emissions allowance and must buy more if they exceed it.
This created a challenge: to avoid EU regulations and costs, some companies moved their CO2-intensive production to countries with lower or no carbon pricing – a practice known as “carbon leakage”.
*This information is summarized editorial content and should not be considered legal advice. VERSO assumes no liability.